Fundamentals of Information Privacy
Foundational knowledge of key Information Privacy concepts
Introduction
This is a summary of notes I made from the Information Privacy course by Infosec and additional research I did on the topic.
There is an overlap of privacy and security and the image below gives you the relationship between them.
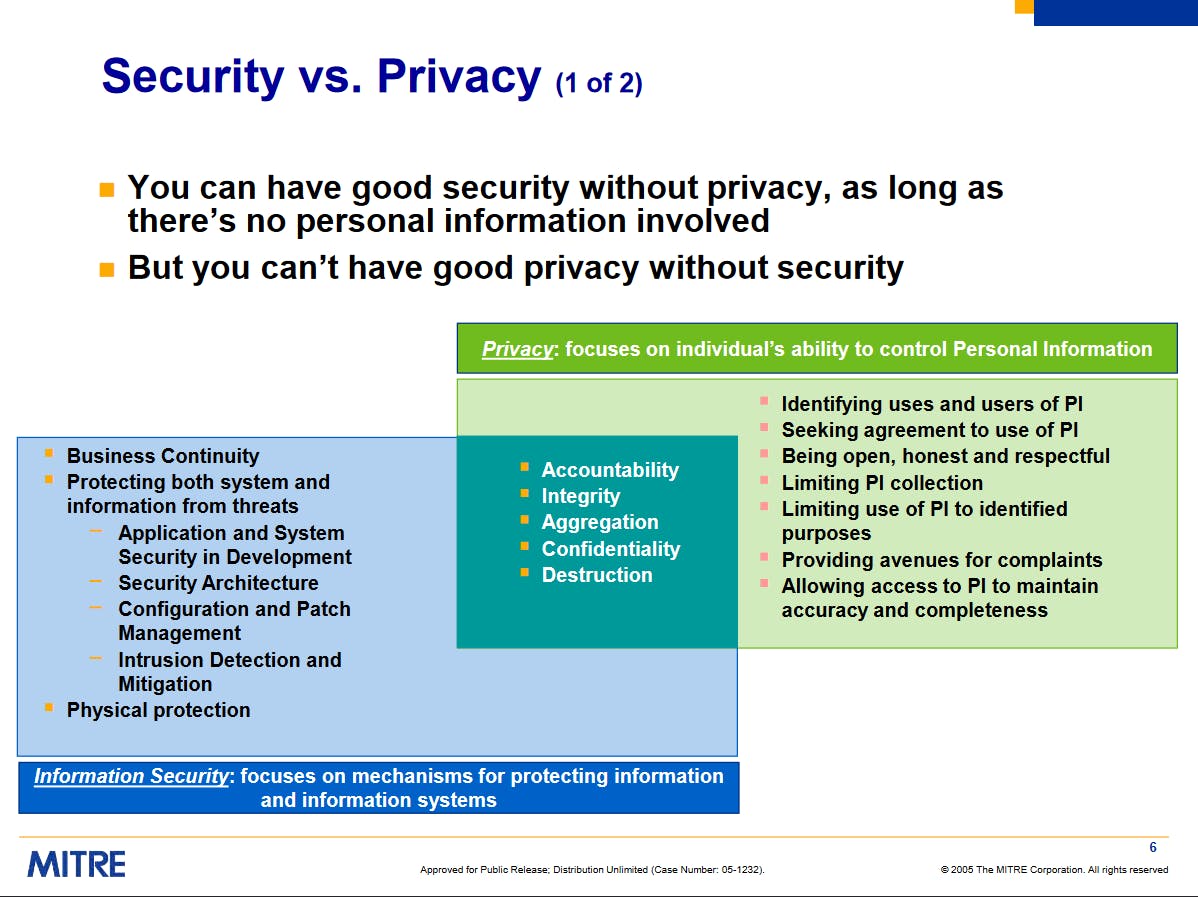
Source: What an Information Security Officer Needs to Know
Personal Information
This includes sensitive and non-sensitive data.
Sensitive Data and Personally Identifiable Information
Protecting sensitive data of users is everyone's responsibility and the disclosure of this data can result in various consequences. To name a few, it affects the welfare of an individual, threatens the security of a nation, jeopardizes goodwill between customers, clients and suppliers, exposes a business to liability etc.
The types of sensitive information include;
Confidential Information- access to this type of information is subject to restriction relative to an individual and/or a business.
Personally Identifiable Information (PII) that could lead to crimes like identity theft or fraud like Social Security Number, Credit Card Numbers, Bank Account Numbers, License Number, Passport Number, National Identification Number.
Health Information- Personal Health Information and Insurance Portability.
Keep in mind that information shared with you by a friend or vice versa in confidence, even though they are not personally identifiable, is also considered sensitive.
However, there is data that can be shared freely with the public and this is known as non-sensitive data. These include
Any report or news that is a matter of public record and knowledge (eg. census records, criminal records, voter registration)
Government-held information that is shared as part of the government transparency and accountability to its citizens.
Routine Business Information like an Earnings report.
Privacy Regulations
Protecting Privacy
Privacy means protecting personal information from disclosure to any unauthorized individual or entity.
It is important to protect the privacy and civil liberties of your staff, clients and anyone you interact with. Organizations must ensure to incorporate privacy protections into their information security planning and put in place better controls to reduce the risk of data being stolen.
This can be done by adopting the Fair Infomation Practice Principles(FIPPs) which is an open framework defining privacy principles and provides guides for their implementation.
Another popular framework for privacy protection is by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development(OECD).
General Data Protection Regulation-GDPR
This represents the EU Law on data protection and privacy and applies to the European Union States and citizens of the member states.
Requirements are as follows:
Lawful, fair, and transparent processing of data
Limitation of purpose, data or storage (ie. keep only data that you need for a specific purpose)
Protect Data Subject(the customer/client) Rights
Have Consent
Report in a timely manner Personal data breaches
Privacy by design
Data protection impact assessment
Data Transfer (example, use of SSL/TLS Certificates)
Have a Data Protection Officer to act as an enforcer.
Awareness and Training for staff
For more information on protecting data subjects, read more on the EU Charter of Fundamental Rights under TITLE II-FREEDOMS, Article 8.
Privacy Controls
Data Management
Managing sensitive data is critical. It is important to develop clear policies that manage data appropriately and protect your organization. These policies defines roles and responsibilities, using data quality procedures through data deduplication by designing storage efficiently.
Database specification and access must be based on user requirements (need to know basis) and the nature of the data which database administrators must audit regularly.
Organizations must prepare and follow a clear data policy and make sure to maintain a proper documentation of data, in other words, inventory to easier tracking and usage whenever needed.
Data Security Controls
When it comes to securing data, controlling access to resources is one of the primary things while protecting the key concepts of information security: Confidentiality, Integrity and Availability of the resources(The CIA Triad).
Two important security controls used by organizations for provisioning systems or users after proper identification and authentication are;
Need-to-Know - user's needs to have access to specific resources.
Least privilege - Granting users only the accesses they need to perform their duties or tasks.
For in-depth basic understanding of privacy and data protection laws, you can read the additional information provided by the International Association of Privacy Professionals IAPP Glossary and a series of articles, white papers, reports and surveys IAPP Privacy 101 series.
You can find all resources here.
Thank you for reading!
